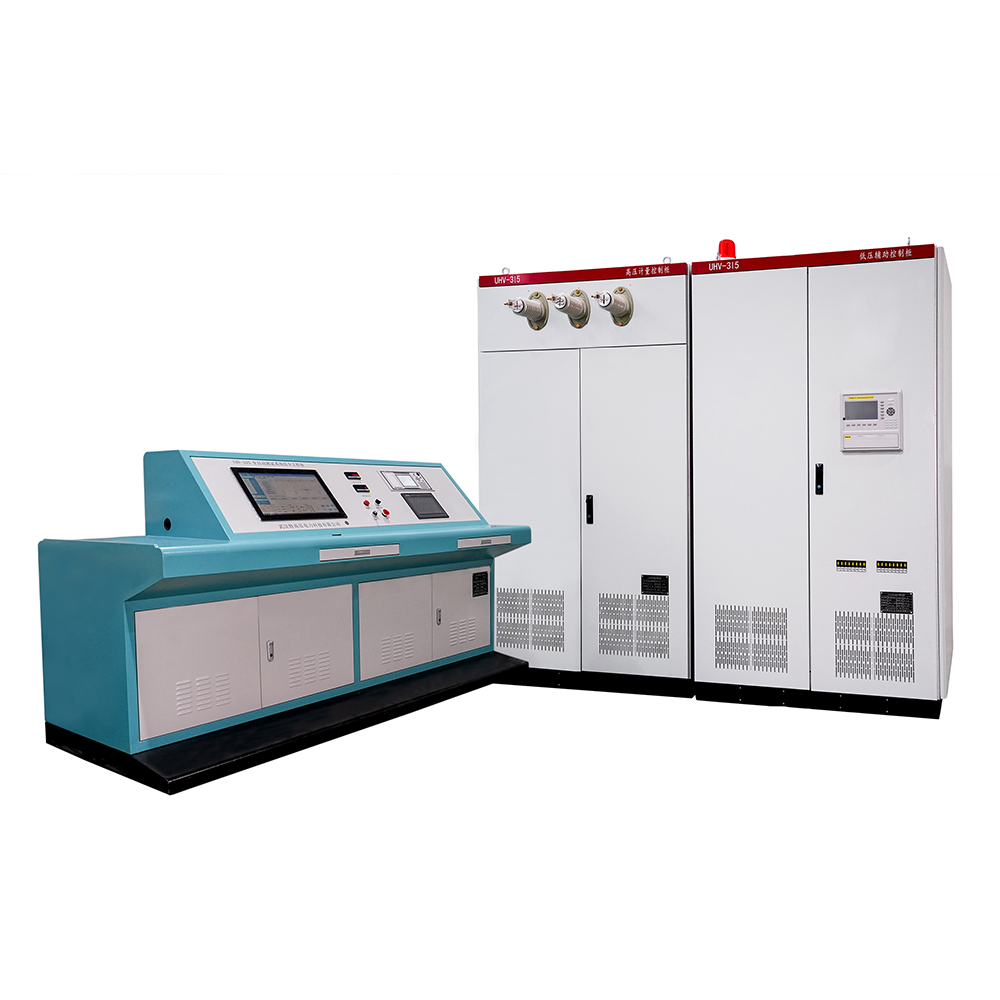
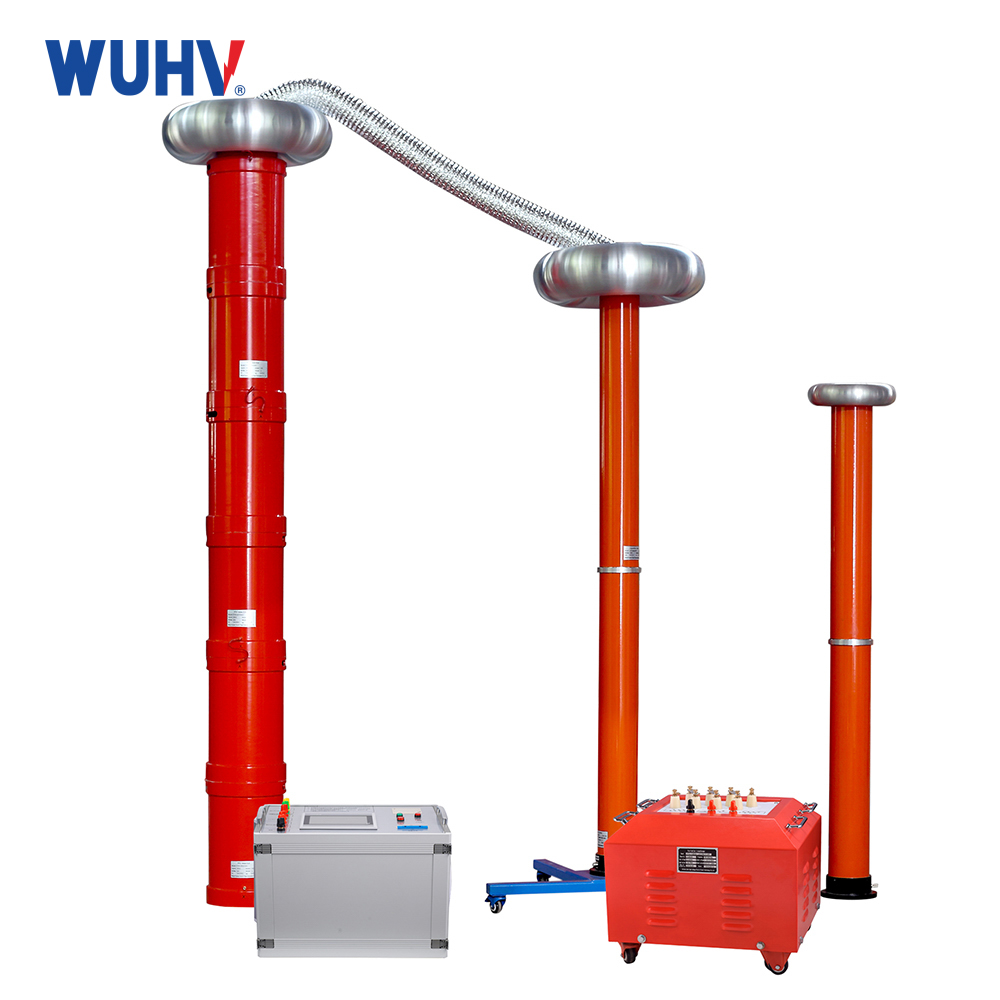
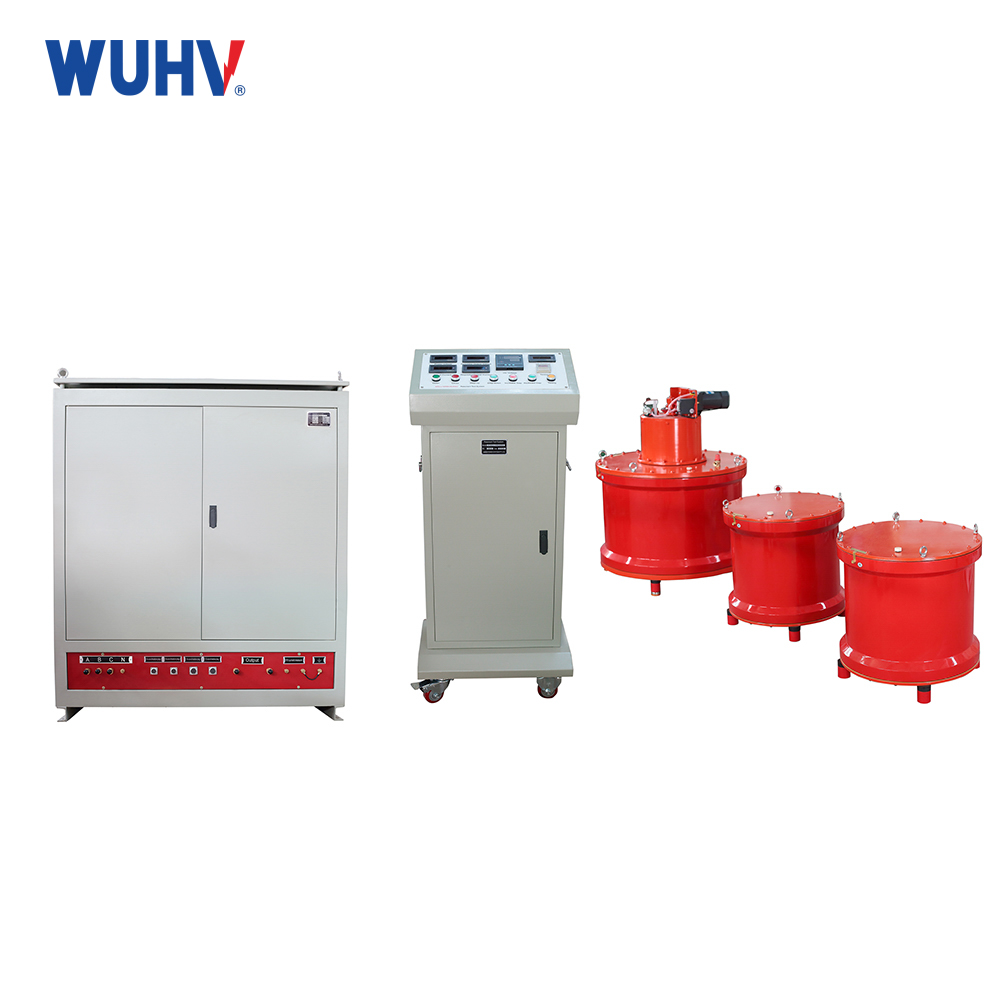
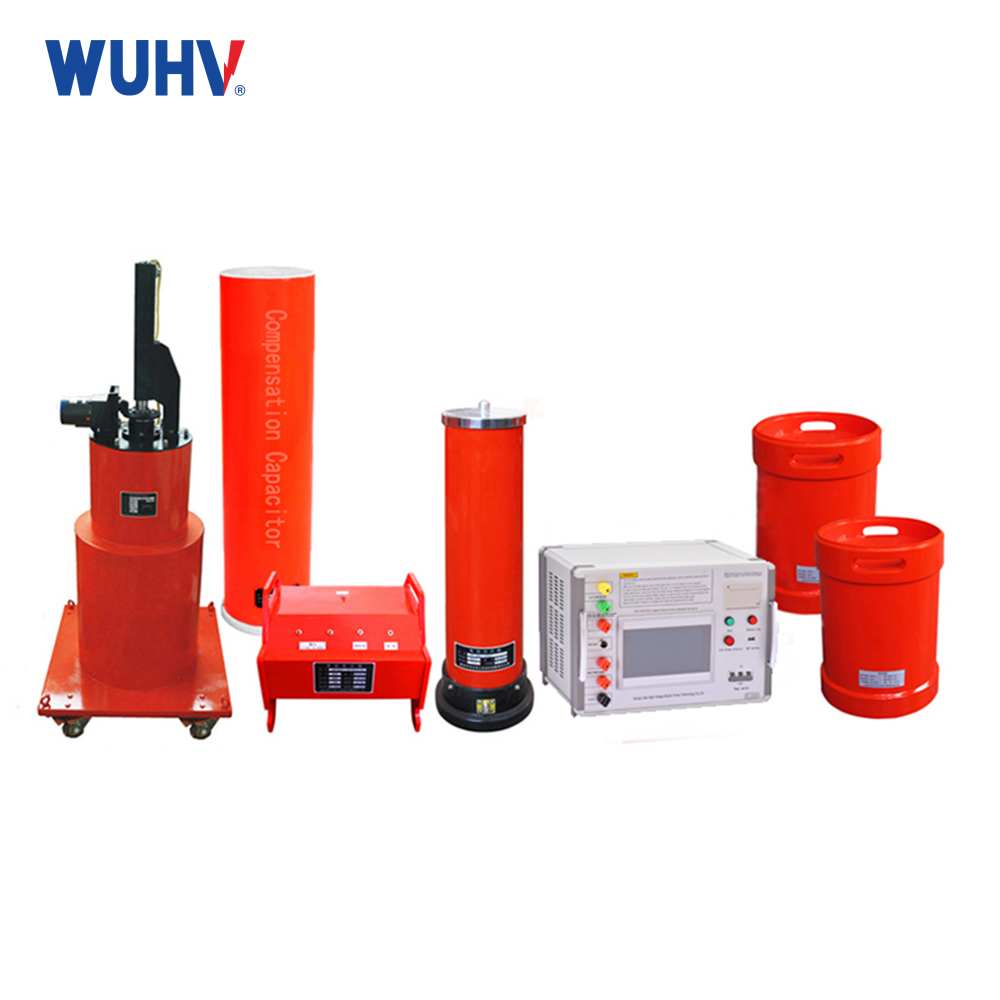
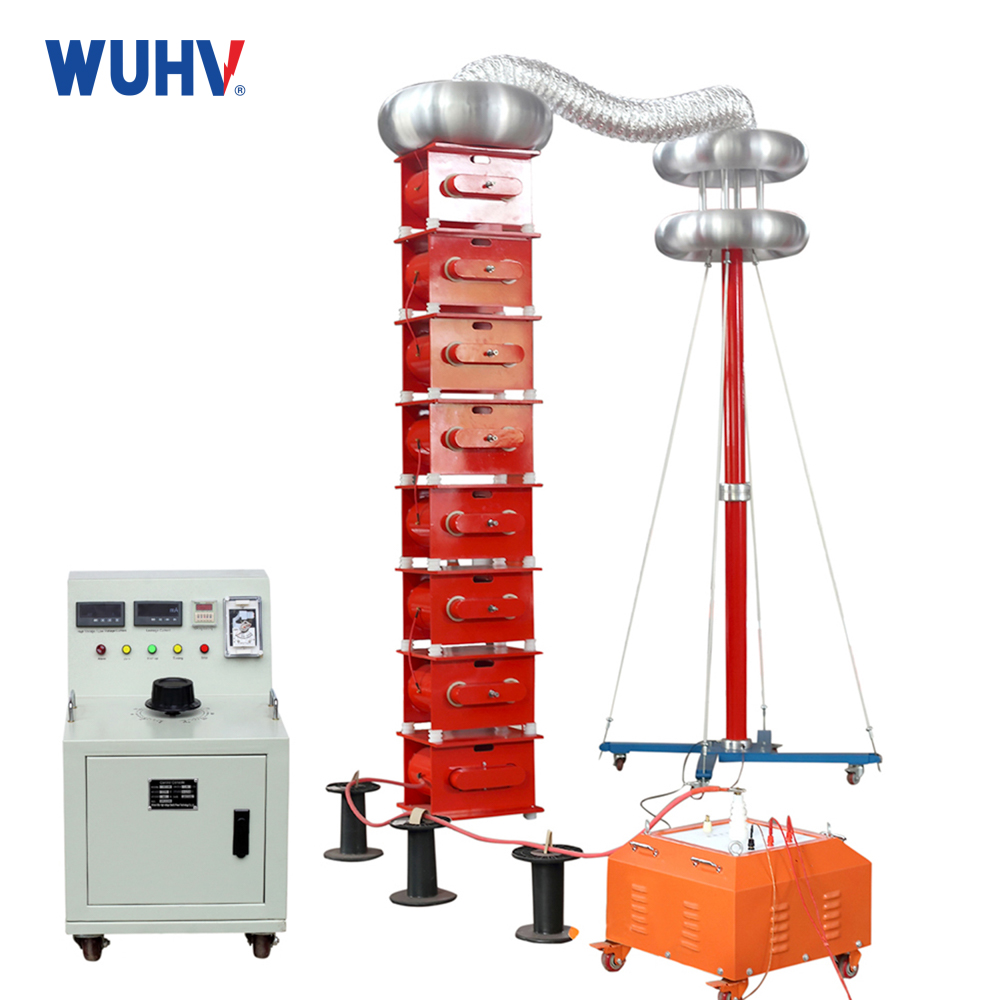
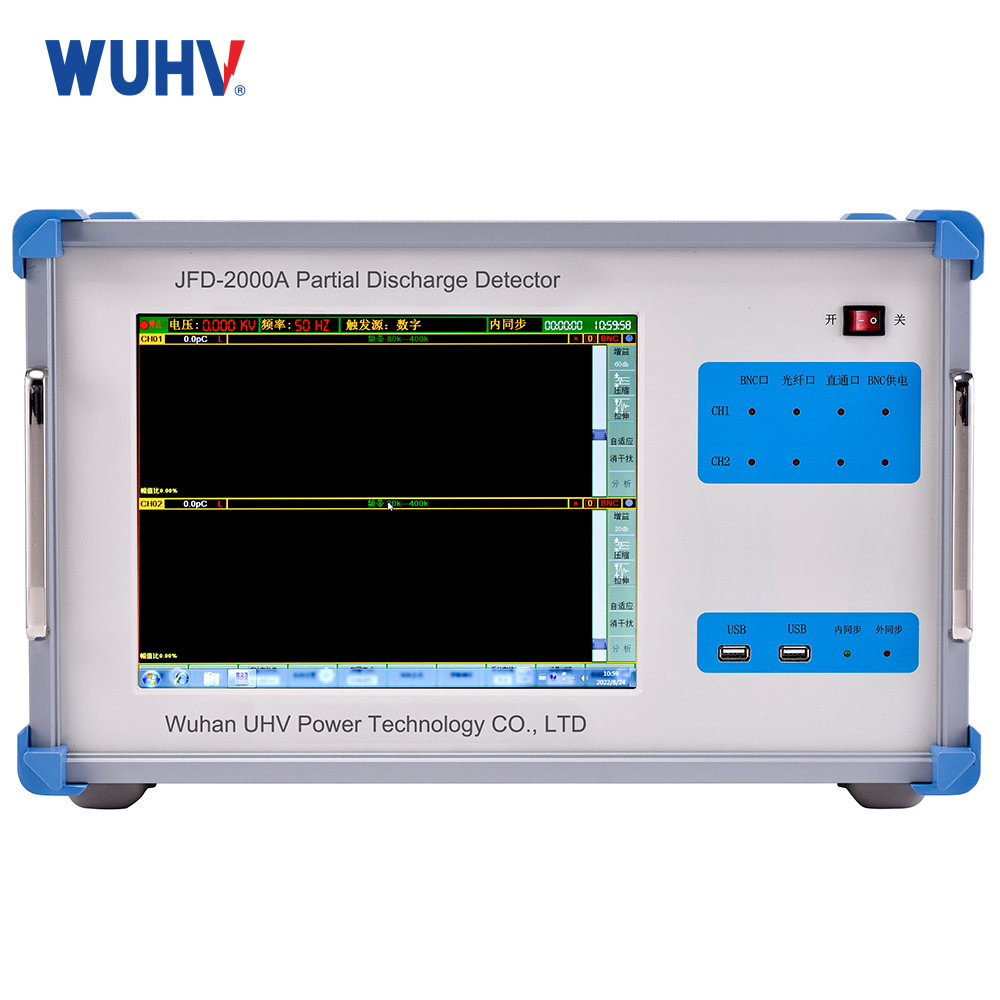
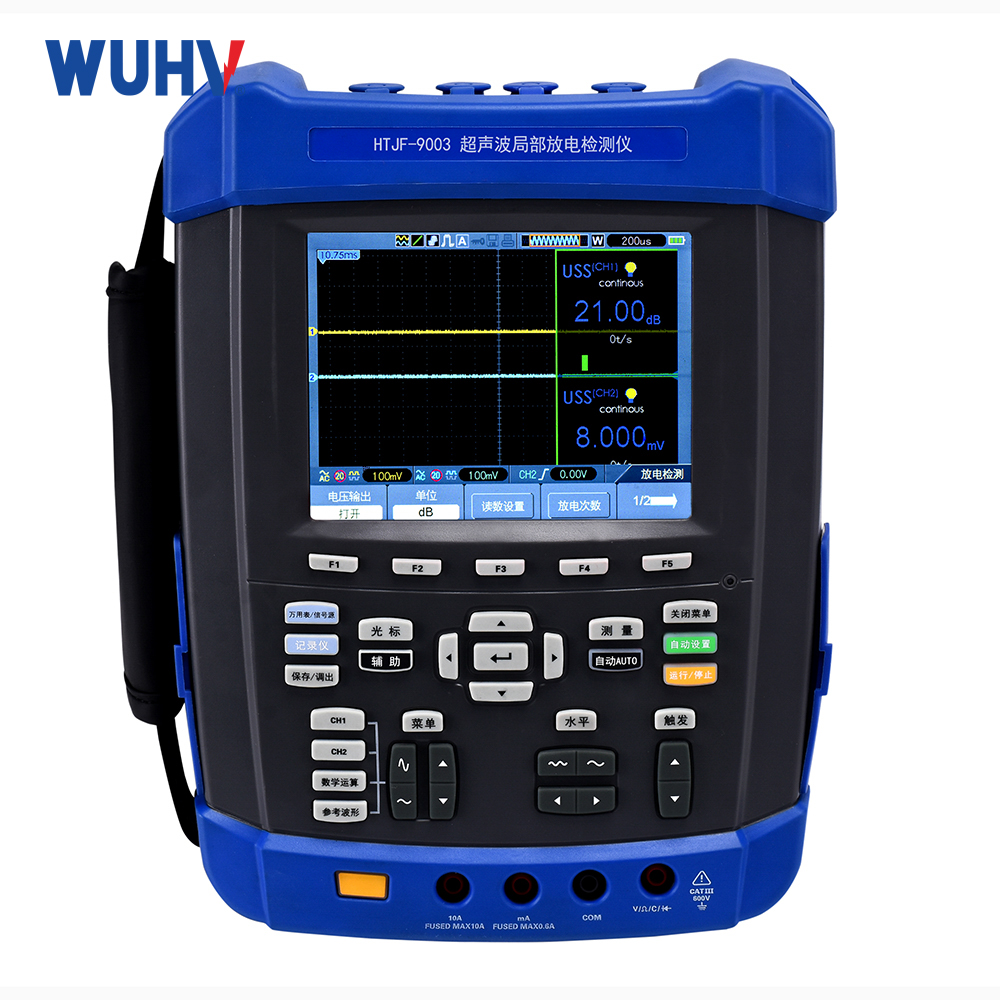
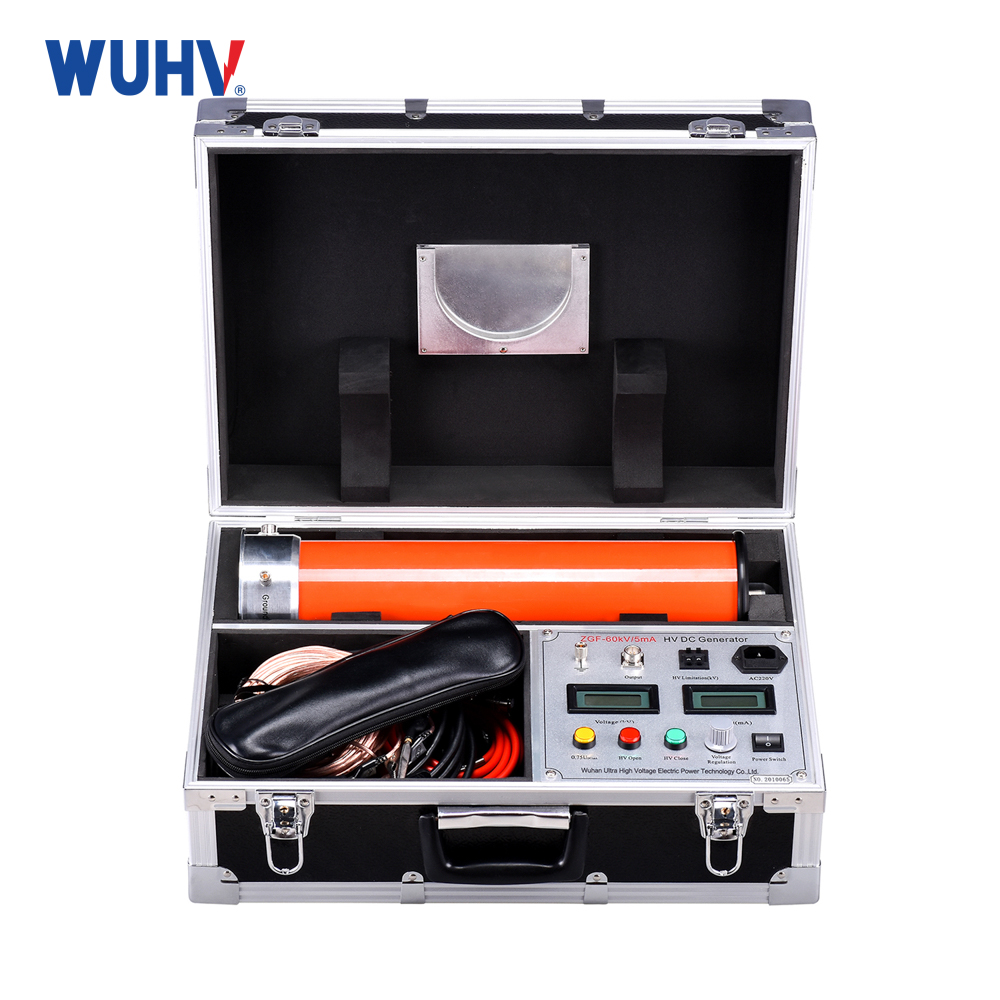
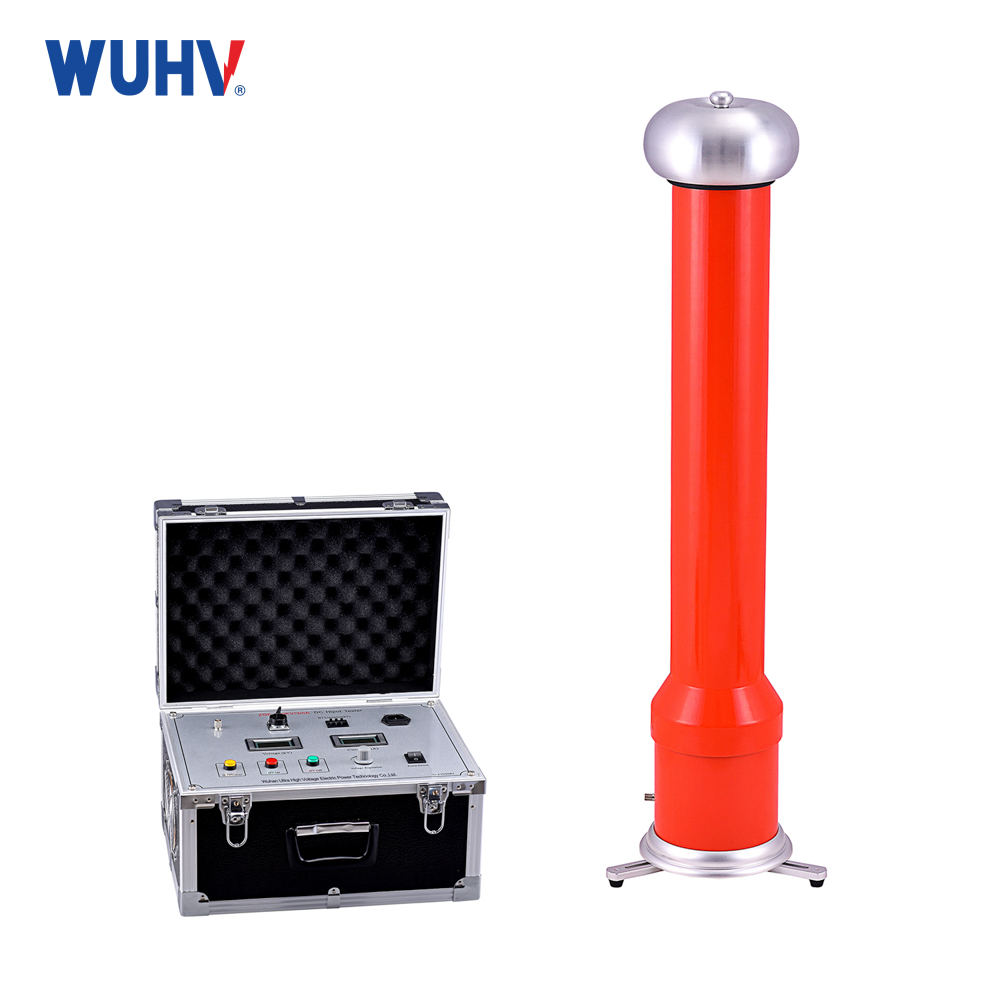
The Transformer Test Bench under Wuhan UHV can help many power workers conduct various power tests more conveniently.
An Electrical Test Bench is a comprehensive platform used for testing, verifying, diagnosing, and evaluating the performance of various electrical equipment, components, systems, or circuits. Its scope is broader than a Motor Test Bench, encompassing not just rotating machines (motors/generators), but also transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, relays, contactors, controllers, power supplies, wiring harnesses, cables, electronic circuit boards, and even entire electrical systems.
Core Functions & Test Items
1.Performance Characterization:
Input/Output Characteristics (voltage regulation, load regulation, efficiency).
Start-up/Shut-down Characteristics.
Steady-State and Dynamic Response (e.g., response to load/input steps).
Power Factor Correction (PFC) Performance.
Output Ripple & Noise.
2.Safety & Compliance Testing:
Insulation Resistance Test: Verifies insulation integrity.
Dielectric Strength (Hipot) Test: Verifies insulation withstand capability (AC/DC/Impulse Hipot).
Ground Continuity Test: Ensures protective earth connection reliability.
Leakage Current Test: Assesses safety risk.
Arc Testing (for switchgear): Validates arc quenching and internal fault protection.
Ensuring compliance with standards (IEC, UL, CSA, GB, EN, etc.).
3.Functional Verification & Logic Testing:
Verifying operation logic and timing of relays, contactors, PLCs, protection devices.
Testing switch/breaker opening/closing characteristics, time-current curves.
Validating control circuit logic.
4.Protection Function Testing:
Testing threshold and response time of OV/UV/OC/SC/OT/phase-loss protection, etc.
Verifying relay protection settings and operating characteristics (distance, differential protection).
5.Environmental Testing:
Testing electrical performance under controlled temperature/humidity (e.g., temperature rise, cold start).
6.Durability & Life Testing:
Long-term operation, switching cycles, accelerated aging to assess reliability/lifespan.
7.Fault Diagnosis & Location:
Testing faulty equipment to analyze causes (e.g., short circuits, open circuits, component failure).
8.EMC Pre-Compliance Testing:
Basic conducted/radiated emissions and immunity pre-assessment (full EMC typically in specialized labs).